Oral surgery
- Bone replacement from own blood (PRF Technology)
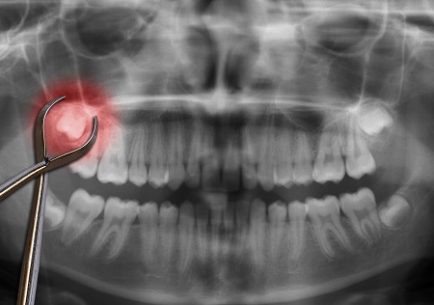
- Tooth extraction
- Wisdom tooth surgery
- Resection of the root apex
- Cyst removal
- Bone graft (replacement)

Services
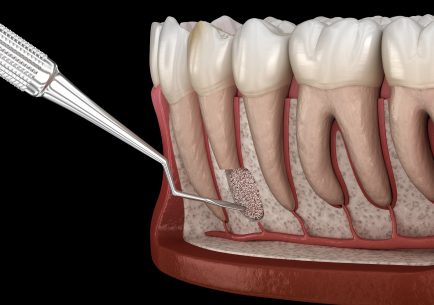
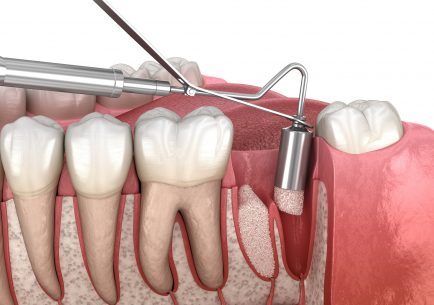
Bone replacement from own blood (PRF Technology)
A few decades ago, people realized that their own blood helps the human body to heal optimally. The essence of this revolutionary new technology is that bone and tissue replacements are performed with plasma made from the patient’s own blood instead of synthetic bone replacements. Compared to traditional bone substitutes, this “own material” is more beneficial because it is full of agents that stimulate regeneration, e.g. with growth factors, fibrin, white blood cells, which are impermeable to bacteria.
Procedure:
- Laboratory tests before surgery: laboratory tests for certain blood parameters are recommended 1-2 weeks before surgery.
- Blood sampling: Immediately before the operation, depending on the size of the intervention, we take 2-8 tubes of blood from the patient.
- Centrifugation of the collected blood: the blood is centrifuged in a special device. As a result, its cellular elements separate into red blood cells and white blood cells. We use the latter for the surgery.
- The gelatinous substance obtained in this way is implanted in the surgical area by itself or mixed with a bone substitute.
Advantages of the procedure: The heaing is almost half comared to the tradicional methods.
- In most cases, the healing is almost half compared to the traditional methods.
- Thanks to the faster recovery, the feeling of well-being after surgery is also significantly better.
- From a material point of view, since the method has at least halved the price of previous larger bone replacements, patients can access these interventions more cheaply.
- There is no risk of rejection: it is not a foreign bone substitute that enters the body, but the material produced by the patient’s body itself.
- After tooth extraction, inflammation can be avoided by placing it in place of the tooth extraction.
- The original size and size of the jawbone can be maintained, because the surrounding tissues suffer significantly less degeneration, the blood vessels and nerves weave through the area many times faster, giving the opportunity for easy insertion of the future implant (socket preservation).
We recommend it for all surgeries!
Contraindication:
- taking stronger anticoagulants;
- malignant hematopoietic disease.
Press Release

Bone replacement from own blood
GGDent Innovative Implantology and Dentistry, which has moved to 30 Fő fasor, has expanded its range of services with a new method as a leader in innovative technologies. During the PRF technology, bone and tissue replacement is carried out with a blood product obtained from the patient’s own blood. On the topic, we talked with Dr. Gábor Görög, oral surgeon dental specialist and implantologist.
Délmagyarország Health magazine annex 2024.03.30.

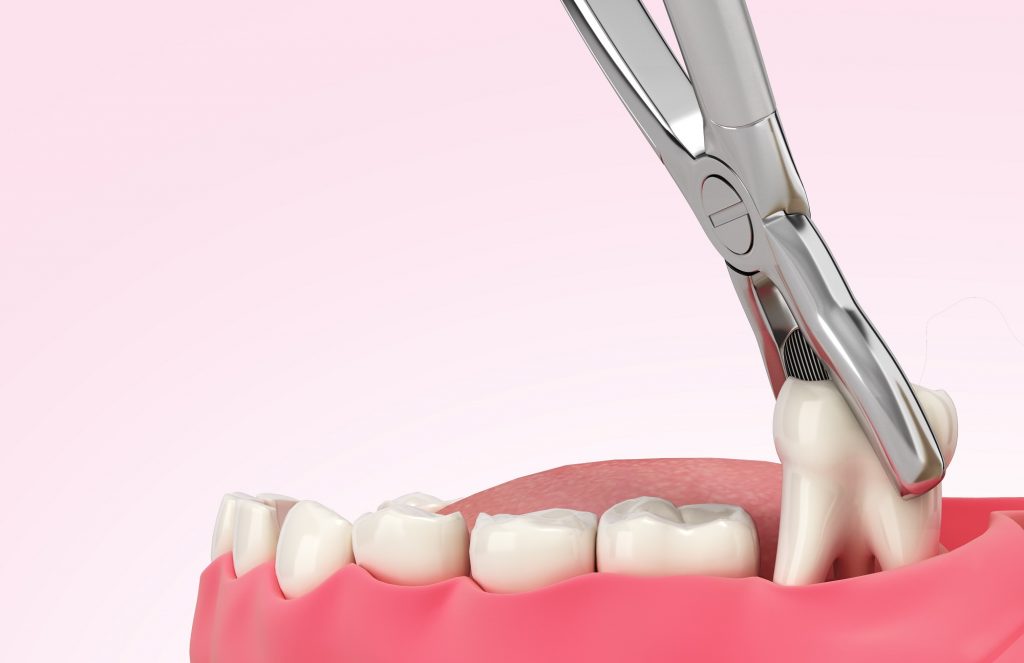
Tooth extraction
By this dental intervention we mean simple (classic) or more complex tooth extractions. It is usually performed next to local anaesthesia and the teeth are removed in a few movements. At the patient’s request, conscious sedation can be used. One or several teeth may be removed, there is no limit to the number of teeth that can be extracted at one time. However, there may be cases where the amount of anaesthetic used means that it is not possible to perform the procedures on both sides at the same time.
Wisdom tooth surgery
Wisdom teeth cause problems for many people throughout their lives. People who often have an inflamed or decaying wisdom tooth may want to have it extracted so that it does not cause problems in the future. There are basically two ways to have it removed:
- if there is adequate access, the tooth can be removed with a pliers after anaesthesia.
- If the tooth is decayed, broken, fragmented or has other complicating conditions, an oral surgeon can remove it properly.
The tooth is removed under anaesthesia and the patient feels no pain during the procedure. In all cases, at least one panoramic X-ray is required before the procedure, and in some cases a CT scan may be required as an additional measure to assess the risks.

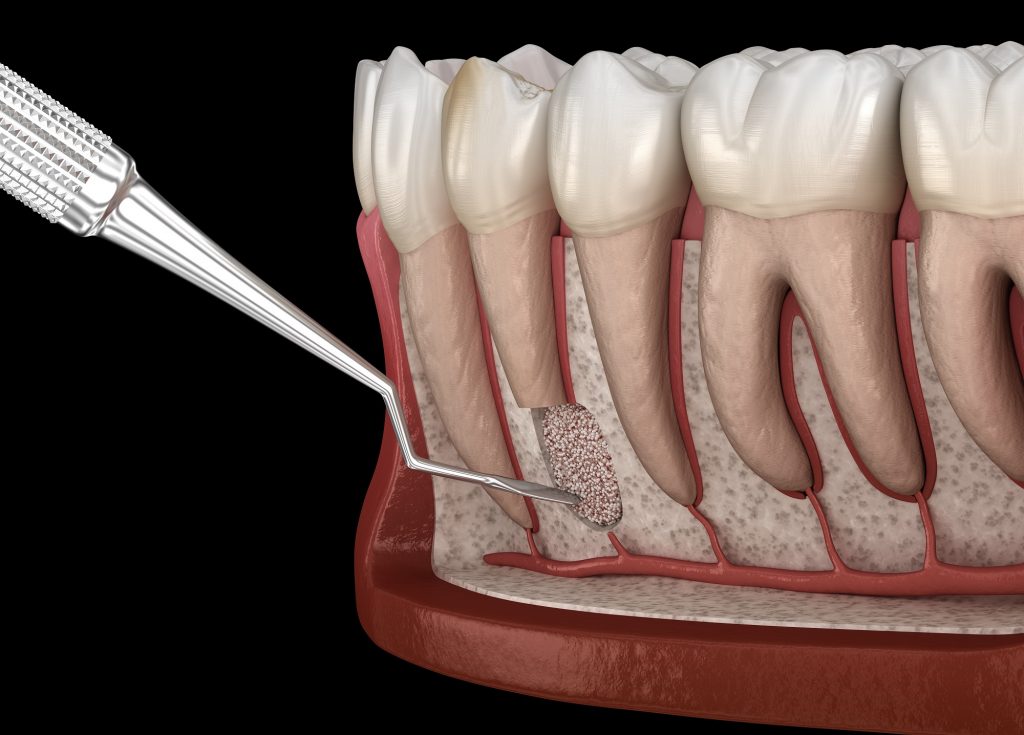
Resection of root apex
Root apex resection is the last option to save a tooth that has undergone root canal treatment. If it is possible to perform the root canal filling correctly, but still there is inflammation or a cyst at the apex of the root, a simple surgical procedure lasting about ten minutes is used to remove the end of the root of the tooth, clearing out the cavity of the inflammation as well.
The procedure is important if you want to save an existing dental bridge or replacement – due to an inflamed tooth – preferably without replacing the crown or tooth abutment. The success of the intervention depends to a large extent on the previously prepared root filling.
Cyst removal
Cysts are foci in the body. They are a pocket formed by bacterial mass, which is lined with epithelium to allow the body to defend itself against pathogens and prevent them from entering the bloodstream. It is essentially a chronic, painless lesion, but occasionally it can swell and become painful due to acute inflammation.
There can be several causes of cyst formation, in dentistry in most cases it is caused by necrosis of the dental pulp. The intervention required is usually root canal treatment. Given that the pathogens originate from the inside of the tooth, cleaning it out leads to a reduction in the size of the cyst. If this is not enough, or if the cyst is too large, it is surgically removed, possibly by drainage, to make it easier for the body to fight off the pathogens.

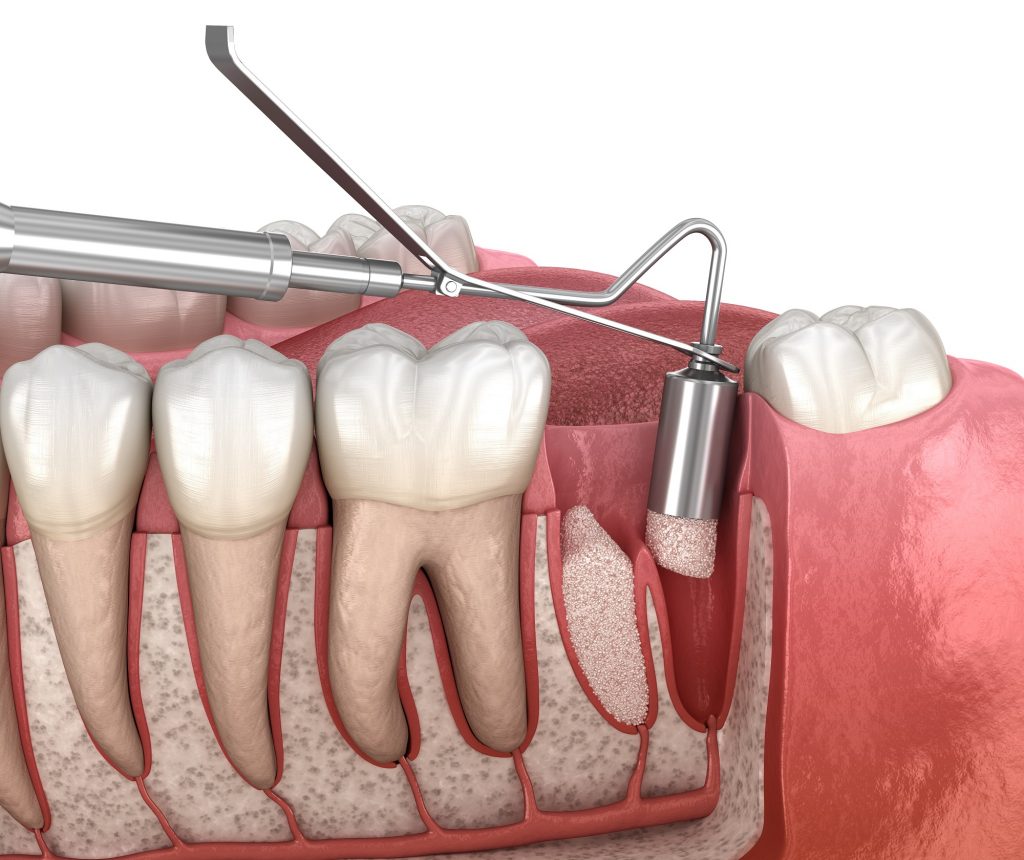
Bone graft (replacement)
Many patients put off having their teeth getting treatment, and the necessary dental procedures and possible extractions as well until the bone itself, which would have served as a supporting bone in the event of a tooth implant, is damaged. The first step in detecting this is to take a panoramic CT scan. On the basis of this scan, the dentist will decide whether bone replacement is necessary and whether to proceed.
Bone grafting is done if there is not enough bone available for an implantation. In this case, we increase the volume using different, individual techniques. After successful bone grafting, the implant can be placed in this replaced layer and the tooth replacement process can begin. In most cases, 4-6 months must pass for healing to be complete after the bone graft, but in other cases the bone graft itself can be carried out at the same time as the implantation. This can depend on many things, such as the patient’s build, habits, gender, medical history, etc. We prefer to avoid bone grafting whenever possible. In all cases, implantation is best when the patient’s own living bone is used. The material of the bone substitute can be synthetic, human or animal, but the most important thing is that it is a lifeless bone. Therefore for about a year after implantation, there is no proper circulation in it, which could otherwise give a chance for infection.
The potential risk is on average 20%, depending on the case, but in very extreme cases it can be up to 60%. However, there is no doubt that for many patients, a tooth implant without a bone graft would be completely out of the question.
Press Release

Dental bone replacement is now a routine procedure
Many patients are horrified when they hear the word bone replacement, even though it is now considered a routine intervention in dentistry. Bone replacement technologies and materials have developed a lot in recent years. If the patient goes to an office with adequate expertise and modern equipment, there is nothing to fear. GGDent nnovative Implantology and Dentistry is such a place.
Délmagyarország Health magazine annex 2023.10.28.